

Other authors /3/ are of the opinion that a thorough examination, even of effusions involving small joints, should be carried out on a routine basis in all patients with joint diseases. The examination of SF can be used as the sole diagnostic criterion only in cases of gout, pseudo-gout, other crystal depositions, and septic arthritis /2/. The clinical value of SF analysis is controversial but its role as an additional diagnostic aid has undoubtedly been recognized.

Synovial fluid (SF) analysis is of interest for the rheumatologist, orthopedic surgeon, and physician because numerous biochemical, cytological, and immunological SF alterations occur in many rheumatic diseases. Articular cartilage works as a lubricant cavity and offers its role, along with synovial fluids, as the boundary lubrication, while the water component of the synovial fluid squeezes out / 1/. It provides a nearly frictionless movement and acts as a shock absorber and plays an important role in the healing process after surgery. Usually, a healthy synovial fluid is considered as the best lubricant to the natural hip or knee joints. Gerald Partsch, Mirjam Franz, Rudolf Gruber, Lothar Thomas – Table 49-7: Effusions classified according to specific joint diseases – Table 49-3: Disorders causing hemarthrosis and hemorrhagic SF – Table 49-8: Laboratory findings in SF, classified according to specific joint diseases – Table 49-6: Synovial fluid findings in joint diseases – Table 49-4: PMN counts in dependence of joint disease
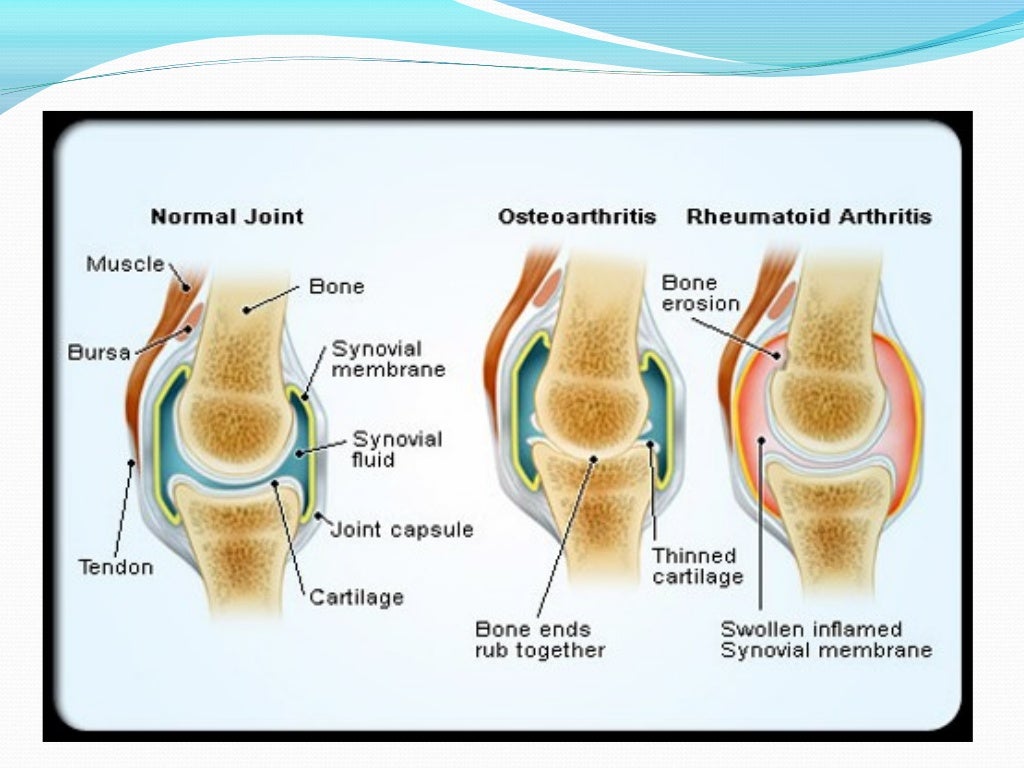
– Table 49-1: Diseases with joint effusions and their classification into four major categories – Table 49-9: Clinical and laboratory findings in inflammatory arthritis In addition, people with certain medical conditions such as gout and rheumatoid arthritis can be more prone to develop olecranon bursitis.13 Homocysteine, vitamin B 12, folates, vitamin B 6, choline, betaineġ4 Gastrointestinal and pancreatic functionġ7 Thrombocytopenias and thrombocyte function testingĢ2 Multiple myeloma and related plasma cell proliferative disordersĢ4 Laboratory and clinical assessment of the complement systemĢ6 Immunogenetics: clinical and diagnostic aspects of the Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) systemĢ9 Cancer associated syndromes (para neoplastic syndromes)ģ1 Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS)ģ2 Pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neuroblastomaģ4 Disorders of the pituitary-adrenocortical axisģ5 Disorders of the pituitary-somatotroph axisģ7 Disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axisĤ6 Laboratory diagnosis of neurological diseasesĥ0 Standardization and quality assurance of quantitative determinationsĥ1 Effect of physical exercise on laboratory test resultsĥ2 Selected analytical laboratory techniques In addition to athletes and students, people in other occupations where olecranon bursitis has been shown to occur more frequently include plumbers, miners, mechanics, and gardeners. Olecranon bursitis can also occur in people who rest their elbow on a hard surface for a long period of time, including when typing on a computer keyboard, and is commonly known as “student’s elbow.” This can occur during any sporting event when someone has a fall on their elbow and has been described often in football, hockey, basketball, and volleyball players. This condition is termed elbow (olecranon) bursitis.Ī common cause of olecranon bursitis is trauma, such as falling on the elbow or hitting the elbow on a hard surface. However, the bursa can fill with extra fluid and become swollen if it becomes irritated or inflamed. Normally, this sac has only a minimal amount of fluid in it and the bursa acts as a cushion for the tip of the elbow. The elbow (olecranon) bursa is a thin sac of fluid that lies between the boney tip of the elbow in the back of the arm (the olecranon) and the skin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
